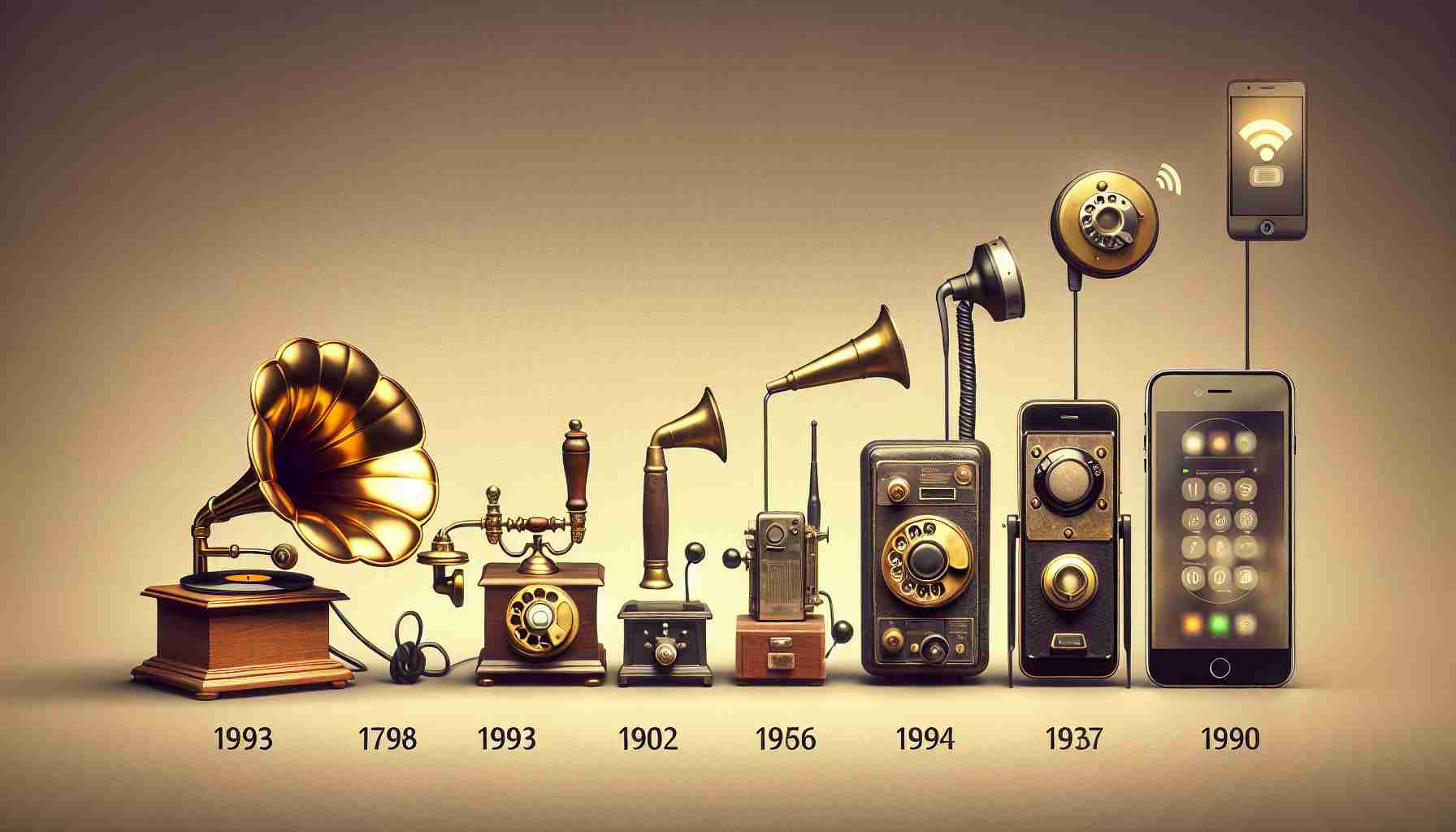
The Emergence of Global Connectivity Through Technology
The rapid adoption of smartphones appears remarkable yet, it is a result of continuous technological evolution. The path to this global connectedness dates back to the phonograph’s inception, which provided unfiltered contact with wider culture. The subsequent introduction of radio and television escalated this process. Each innovation reduced barriers until the smartphone emerged, unifying private and universal experiences conveniently in one’s palm.
In the 20th century, there was a trend of balancing a need for personal liberation from reality with the desire to experience it “virtually.” Technologies progressed to satisfy a deeply rooted urge for self-cultivation and social engagement during leisure time. This journey from phonograph to smartphone has mirrored societal shifts towards instantaneous gratification, pushing aside the more deliberate pursuits of previous generations.
Technology and Free Time: An Insight into Modern Leisure
The intricate tapestry woven by the internet transcends the limitations of time and space. It has democratized access to knowledge and entertainment that was once limited to tangible forms. Digital clouds and the internet facilitate almost instantaneous connections to extensive resources. Particularly in America, these technologies have become necessary for maintaining relationships, highlighted by their invaluable role during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The digital era has also fostered a redefinition of individuality and social interaction, particularly among youth. The vehicle once stood as a teenage rite of passage, but the virtual spaces provided by the internet now replace the need for physical gatherings.
Overall, the progression of digital technology from its earliest forms to the modern smartphone tells a story of humanity’s quest for a harmonious balance between solitude and social exploration. This ongoing journey underscores the power of connectivity and the ever-evolving landscape of how we engage with the world around us.
Relevant Facts to the Topic:
– The evolution of connectivity technology has been marked by a series of revolutionary inventions that includes the telegraph and the telephone, both of which preceded the phonograph. The telegraph, patented in 1837 by Samuel Morse, was the first device to allow long-distance transmission of messages. The telephone, invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876, transformed the concept of real-time voice communication.
– The internet, initially a project commissioned by the United States Department of Defense as ARPANET in 1969, has become the backbone of modern connectivity, giving birth to the World Wide Web in 1991, as proposed by Tim Berners-Lee. This was pivotal in globalizing access to information and is the foundation for the connectivity we enjoy in the era of smartphones.
– Social media platforms have significantly influenced the evolution of connectivity, with companies like Facebook (now Meta), Twitter, and Instagram reshaping how people communicate and share information.
– Smartphones have integrated various technologies such as GPS for navigation, high-definition cameras for photography, and sensors for health monitoring, making them multifunctional devices beyond basic communication tools.
Key Questions and Answers:
– What are the societal impacts of the shift from physical to virtual interactions? The shift has facilitated greater global interconnectedness and access to information but has also contributed to issues like decreased face-to-face social skills, cyberbullying, and digital addiction.
– How has smartphone technology impacted the way we work? Smartphones have enabled flexible working conditions, including remote work and the gig economy, but they have also led to longer working hours and the challenge of work-life balance.
Key Challenges and Controversies:
– Privacy and Security: As connectivity has increased, so have concerns over privacy and data security. Smartphones collect vast amounts of personal information which can be susceptible to breaches.
– E-waste: The rapid evolution of technology has led to the generation of considerable electronic waste which poses environmental challenges.
– Access Inequality: Despite the increasing pervasiveness of technology, there remains a “digital divide” where many individuals and communities have limited access to the internet and modern devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
– Advantages: Connectivity technologies have increased access to education, medical resources, fostered democratic participation, and enhanced global awareness. They allow for instant communication and have increased convenience in many aspects of daily life.
– Disadvantages: The overreliance on technology can lead to reduced personal interactions, which might impact social skills. There is also the risk of information overload, reduced privacy, and the potential for spreading misinformation.
Suggested Related Links:
For further exploration into the evolution of connectivity, these links might be useful:
– IBM: Offers insights into the development of computing technology, which has paved the way for the modern internet and smartphones.
– Apple: As a leading smartphone manufacturer, Apple’s site provides information on current smartphone technology and its applications.
– Intel: Reflects the development of microprocessors that significantly contributed to the power of devices we use for connectivity today.
Ensuring that each link directly connects to the main domain without specific subpages or query parameters guarantees the URLs are valid and offers a broad overview of the companies and technologies that have facilitated the evolution of connectivity.