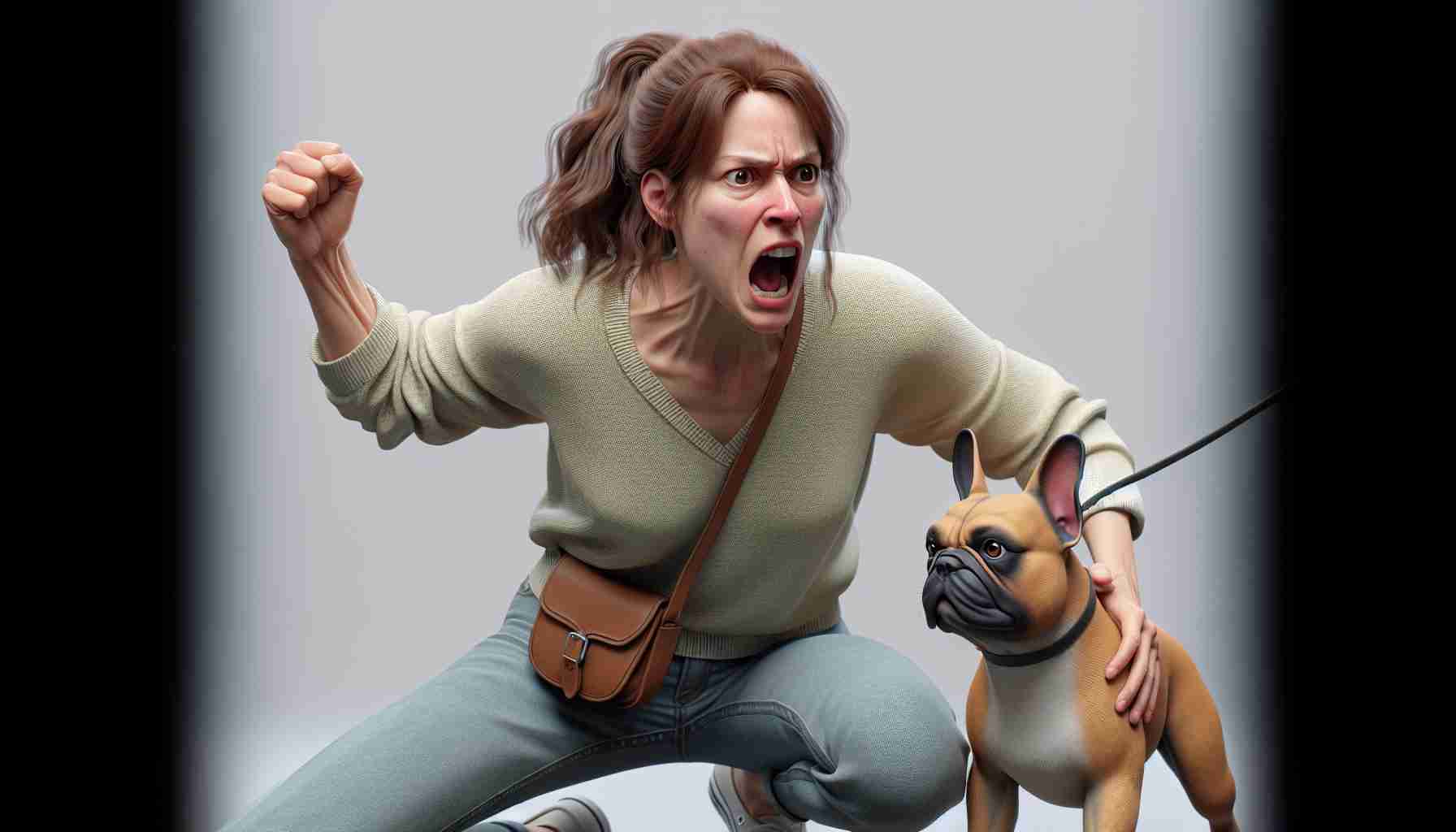
In a surprising legal battle, Manitoba’s Court of Appeal has upheld the conviction of Tannis Lyn Park, who was sentenced for utilizing her pet bulldog as a deadly weapon. At 55 years old, Park faced a grueling trial for the 2022 incident, receiving an 18-month prison term followed by two years on probation.
Park’s defense hinged on the claim that her involvement was limited to directing the animal towards only one victim. However, the court found sufficient evidence to hold her accountable for both attacks, firmly denying her appeal in a decision made public this Thursday.
The court’s ruling solidifies the legal stance that pet owners can be held responsible for using their animals deliberately in harmful acts against others.
—
Severe Monkeypox Strain Hits Manitoba After Traveler Returns
A traveler returning to Manitoba has brought back an unexpected threat—the province’s first recorded incidence of a more severe monkeypox strain. This development, announced in a government release, marks the presence of Clade Ib monkeypox within Canadian borders.
Officials have linked this case to a broader outbreak of Clade I monkeypox currently affecting regions in Central and Eastern Africa. In response, Manitoba’s health department is undertaking rigorous contact tracing to prevent any further transmission of this disease.
The provincial health authorities have emphasized the need for vigilance as they continue their investigation, aiming to curb the spread of this more virulent strain.
The Untold Impacts of Monkeypox on Global Health and Society
Exploring the Global Ramifications of Emerging Monkeypox Strains
The recent identification of the more severe Clade Ib monkeypox strain in Manitoba underscores a growing global health concern. As officials race to track and manage this outbreak, it’s important to consider how this virus affects not just individual health, but also communities and international relations.
What is Monkeypox, and Why is it a Concern?
Monkeypox is a zoonotic virus, meaning it can spread from animals to humans, and it primarily occurs in tropical rainforest regions of Central and West Africa. The resurgence of the virus, particularly the more virulent Clade Ib, poses significant challenges due to its potential for human-to-human transmission, mirroring concerns similar to those seen during the COVID-19 pandemic. The evolution of this virus raises crucial questions about global preparedness and response strategies.
How Does This Impact Communities?
The emergence of Clade Ib monkeypox in regions like Manitoba can disrupt local healthcare systems and prompt public anxiety. Hospitals might experience increased strain as they handle suspected cases, leading to delays and limited resources for other medical needs. Communities could face restrictions if outbreaks become widespread, impacting daily life and local economies.
Advantages of Early Detection and Response
The swift identification of the virus allows for immediate intervention measures, such as contact tracing and quarantine, which are vital in preventing a larger outbreak. Early detection also accelerates vaccine distribution and public education efforts, reducing potential infection rates.
Disadvantages and Challenges
However, there are numerous challenges. The stigma attached to infected individuals can have severe social consequences, while widespread misinformation may lead to panic or skepticism towards health advisories. Additionally, the global supply chain may face disruptions as countries prioritize healthcare resources, affecting economies worldwide.
Interesting Facts and Controversies
It’s noteworthy that while vaccines exist for monkeypox, their availability is limited, and production ramp-up could take months. This has stirred debate on prioritizing vaccine distribution between countries, raising ethical questions about resource allocation. Additionally, public health experts emphasize the importance of understanding the virus’s animal reservoirs, a field requiring more research to prevent cross-species transmission.
Related Links
For more information about monkeypox and other emerging zoonotic diseases, resources like the World Health Organization and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offer comprehensive guidance and updates.
As global populations continue to intertwine, such emerging health threats remind us of the importance of international cooperation and proactive public health strategies. Addressing these concerns effectively not only protects current generations but also fosters a resilient future.