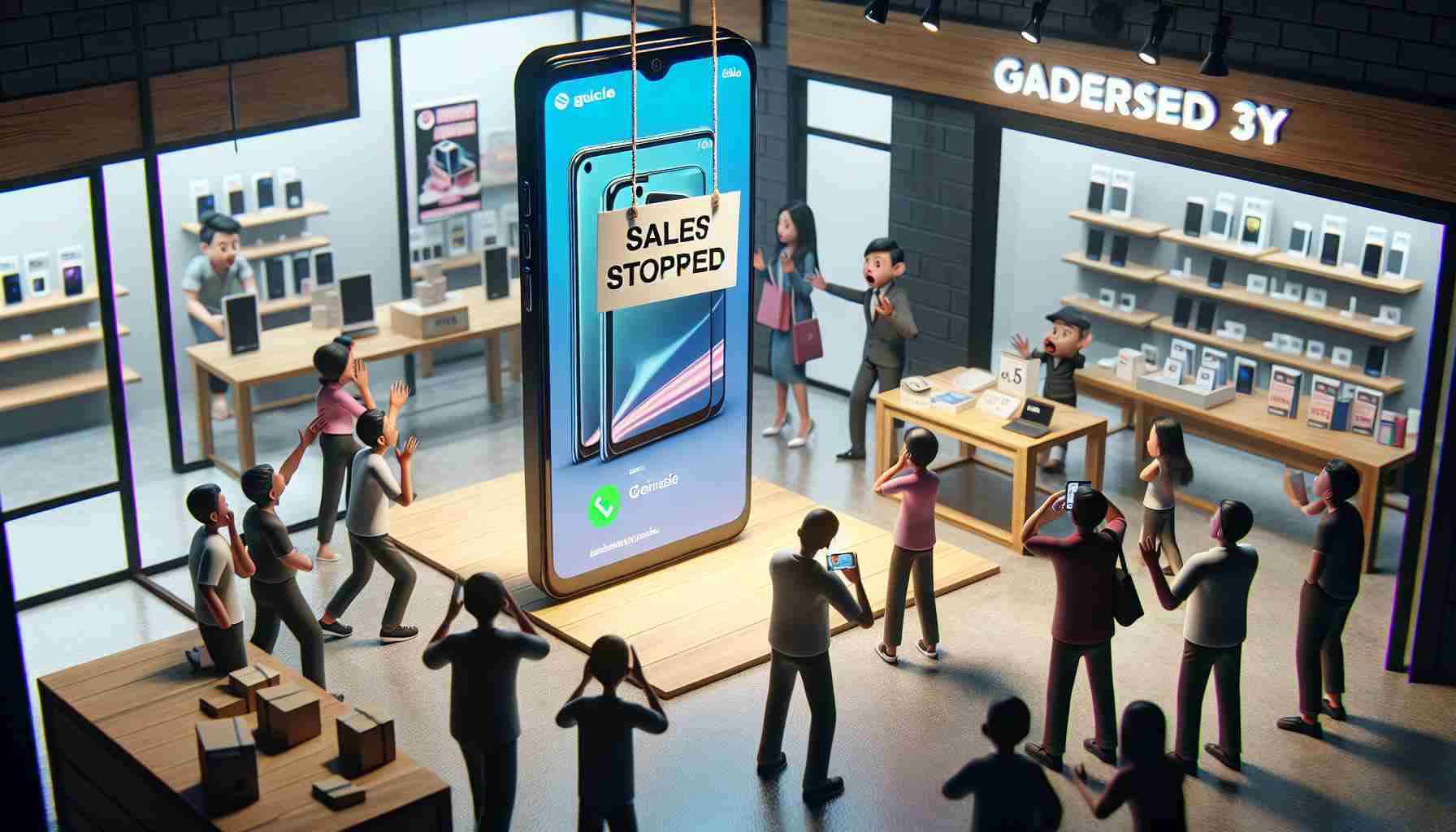
Apple is facing unforeseen challenges in Indonesia as their latest iPhone 16 models remain unsold amidst regulatory hurdles. The country has implemented strict requirements, demanding that devices sold within its borders contain a minimum of 40% Indonesian-sourced components. The certificate required to meet this condition has lapsed for Apple’s iPhone, prompting a halt in sales until compliance is restored.
Investment Shortfall and Local Collaboration
Compounding the issue, Apple is shy of its pledged economic commitment. The tech company previously vowed to invest 1.71 trillion rupiah (approximately $109.6 million) but has only managed 1.48 trillion rupiah ($94.53 million) thus far. As a response, Apple has embarked on creating Apple Academies in Indonesia as part of an innovation development scheme, with three already operational and a fourth announced this past April. These academies aim to nurture local talent and drive app development in the region.
Alternatives and Future Proposals
With the sales ban in place, Indonesian consumers eager to own the new iPhone must resort to purchasing overseas, incurring additional import fees. In a bid to resolve these issues, Apple has proposed an increased investment of $100 million over the next two years, surpassing a previous offer significantly. Meanwhile, Indonesia demands further focus on research and development for locally sold iPhones. The country has also barred Google’s Pixel 9 over similar concerns, suggesting a potential recovery path for both tech giants in a nation vibrant with young, tech-savvy consumers.
The Global Ripple Effect of Indonesia’s Regulatory Battle with Apple
Indonesia’s Stance on Local Content: A Double-Edged Sword
Indonesia’s decision to enforce stringent local content regulations on smartphones has sent shockwaves through the global tech industry. By mandating a 40% threshold of Indonesian-sourced components, the country aims to bolster its local manufacturing industry and reduce dependency on foreign products. While this policy offers potential economic benefits for Indonesia, it also poses significant challenges for international companies like Apple, whose supply chains are intricately tied to multiple countries.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
One of the most intriguing aspects of Indonesia’s regulations is their potential impact on global supply chains. Tech giants like Apple rely on a complex network of suppliers worldwide. The requirement to source a substantial portion of components locally could lead to increased production costs and logistical challenges. This scenario raises questions about the viability of current global supply chain models and whether more countries might adopt similar protectionist strategies.
Balancing Economic Growth with Innovation
The establishment of Apple Academies in Indonesia is a strategic move to foster local talent and drive technological innovation. These academies play a crucial role in empowering young developers, offering them the skills needed to succeed in a competitive digital landscape. However, some critics argue that these efforts might not be enough to offset the economic shortfall and address the immediate sales ban.
The Dilemma for Indonesian Consumers
For Indonesian consumers, the sales ban on the iPhone 16 translates into limited access to the latest technology. This predicament highlights a broader issue faced by consumers in countries with strict import regulations: the difficulty of obtaining cutting-edge technology without incurring hefty import fees. It also prompts a critical question: Should countries prioritize local industry growth at the expense of consumer access to global innovations?
Tech Giants’ Reactions: A Case Study for the Industry
Apple’s proposal to increase its investment in Indonesia by $100 million underscores the high stakes involved in navigating international regulatory landscapes. This move also serves as a case study for other tech companies learning to adapt to varying local regulations. The simultaneous ban on Google’s Pixel 9 suggests a growing trend where global tech firms must rethink their market strategies to accommodate different regulatory environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Local Content Regulations
Advantages:
– Economic Growth: By promoting local component manufacturing, countries can potentially enhance domestic production capabilities and stimulate economic growth.
– Job Creation: New jobs may emerge from increased local manufacturing and assembly activities.
– Technological Advancement: Initiatives like Apple Academies can lead to significant technological advancements and skill development.
Disadvantages:
– Increased Costs: Companies may face higher production costs due to the need to source components locally.
– Limited Consumer Choice: Consumers may have fewer options and face delays in accessing the latest technology.
– Potential Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chains might face unforeseen disruptions as companies adapt to comply with local regulations.
Future Implications: What Lies Ahead?
As technology continues to integrate with daily life, how will countries balance local economic development with global technological integration? Will more nations adopt similar regulatory approaches, and how will tech giants respond? The unfolding scenario in Indonesia prompts critical discussions on the future of international business and technology relations.
For those interested in following these developments further, consider exploring BBC or CNN for more insights into the global implications of local technological regulations.