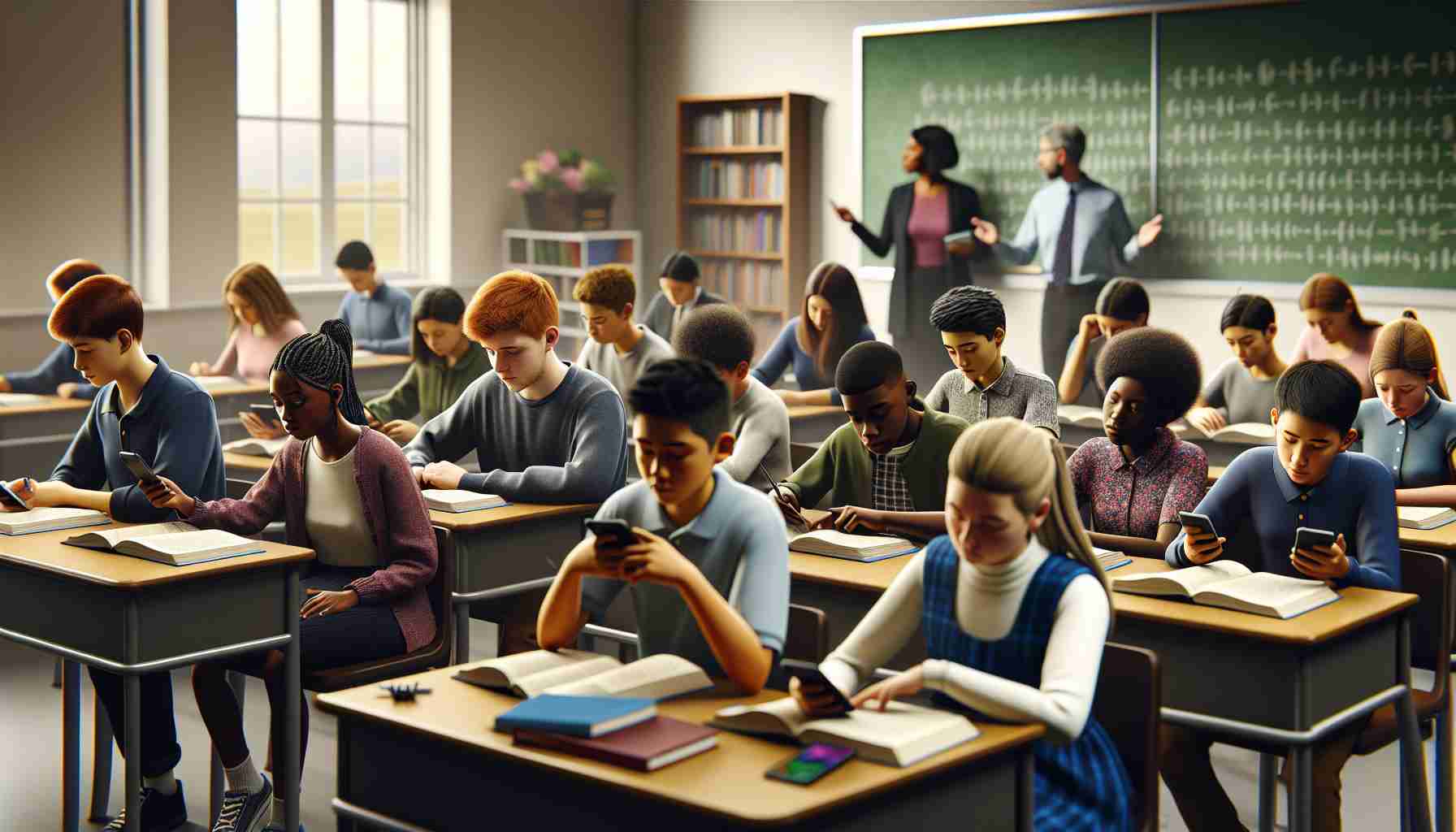
A recent petition has ignited discussions in Italy regarding the regulation of smartphone usage among adolescents. Spearheaded by a group of psychologists and educators, the initiative has garnered considerable attention from notable figures in the Italian film industry, including renowned actors. The core of the proposal emphasizes the notion of prohibiting the possession of mobile phones for individuals under the age of 14 and limiting social media access until the age of 16.
The rationale behind this movement stems from neuroscientific concerns about the adverse effects of early smartphone exposure on cognitive and emotional development. Studies suggest that such early usage may disrupt the balance between real and virtual interactions, negatively affecting social skills and learning capabilities. Several schools across Europe have already observed improvements in student engagement after implementing restrictions on smartphone usage.
A case in point is the Calvijn College in the Netherlands, where a ban on mobile phones was introduced six years ago. Initially met with resistance from students accustomed to using their devices in school, the decision aimed to combat the observed decline in face-to-face communication and collaboration among students. Following the implementation of the ban, the school environment underwent a profound cultural shift, with increased social interactions and improved classroom participation.
Despite some dissent among students, the positive outcomes, such as enhanced focus and a drop in cyberbullying incidents, indicate that such measures could be beneficial. As a result, educational authorities are now considering similar actions as part of a broader strategy to foster healthier educational and social environments.
The Impact of Smartphone Restrictions in Schools: An In-Depth Analysis
In recent years, the conversation surrounding smartphone restrictions in schools has escalated, fueled by a growing body of research and anecdotes from various educational institutions around the globe. As technology continues to evolve, educators are grappling with the implications of smartphone usage in the classroom and its effects on students’ academic performance, wellbeing, and social skills.
Key Questions and Answers
1. What are the primary reasons schools implement smartphone restrictions?
The primary reasons include concerns over distractions in the classroom, reduced face-to-face interactions among students, and the potential for cyberbullying. Educators argue that unfettered access to smartphones can hinder academic focus and diminish student engagement during lessons.
2. What evidence supports the effectiveness of smartphone restrictions?
Several studies have indicated that schools that impose restrictions on smartphone use report improved academic performance and social interactions. For example, a research study conducted by the London School of Economics found that schools which banned mobile phones saw a notable increase in student test scores, particularly among disadvantaged students.
3. What challenges do schools face when enforcing smartphone policies?
One of the major challenges includes resistance from students who feel entitled to use their devices. Additionally, schools must grapple with ensuring fair enforcement of rules, as well as addressing parental concerns regarding communication availability during school hours.
Advantages of Smartphone Restrictions
1. Enhanced Focus and Learning: Restrictions can lead to fewer distractions, allowing students to concentrate better on the lesson.
2. Improved Social Skills: With less reliance on digital communication, students may develop stronger interpersonal skills through direct interactions.
3. Reduced Instances of Cyberbullying: Limiting smartphone use can decrease the avenues through which cyberbullying occurs, fostering a safer school environment.
Disadvantages of Smartphone Restrictions
1. Parental Concerns: Parents may worry about their children’s safety and the ability to communicate in emergencies.
2. Loss of Educational Tools: Smartphones can serve as powerful educational tools; restrictions may hinder the use of beneficial apps and resources during class.
3. Student Alienation: Some students may feel disconnected from their peers who may communicate primarily through social media platforms.
Controversies Surrounding Smartphone Restrictions
The debate on smartphone restrictions often pits the benefits against the perceived need for technology in education. Advocates argue for the importance of fostering an environment conducive to learning, while opponents may highlight the need for equipping students with essential digital literacy skills. Furthermore, the issue of equity arises as students from lower-income households may rely on their smartphones for educational purposes, including internet access and digital resources.
Conclusion
As educational institutions continue to navigate the complex landscape of technology use in schools, the implementation of smartphone restrictions remains a contentious issue. Striking a balance between enabling technology use for educational benefits while addressing the concerns related to distraction and social interaction will be crucial for educators moving forward. Schools must collaboratively work with parents, students, and the community to establish policies that prioritize academic success and mental health.
For further exploration of this topic, visit Edutopia for resources on technology integration in education.