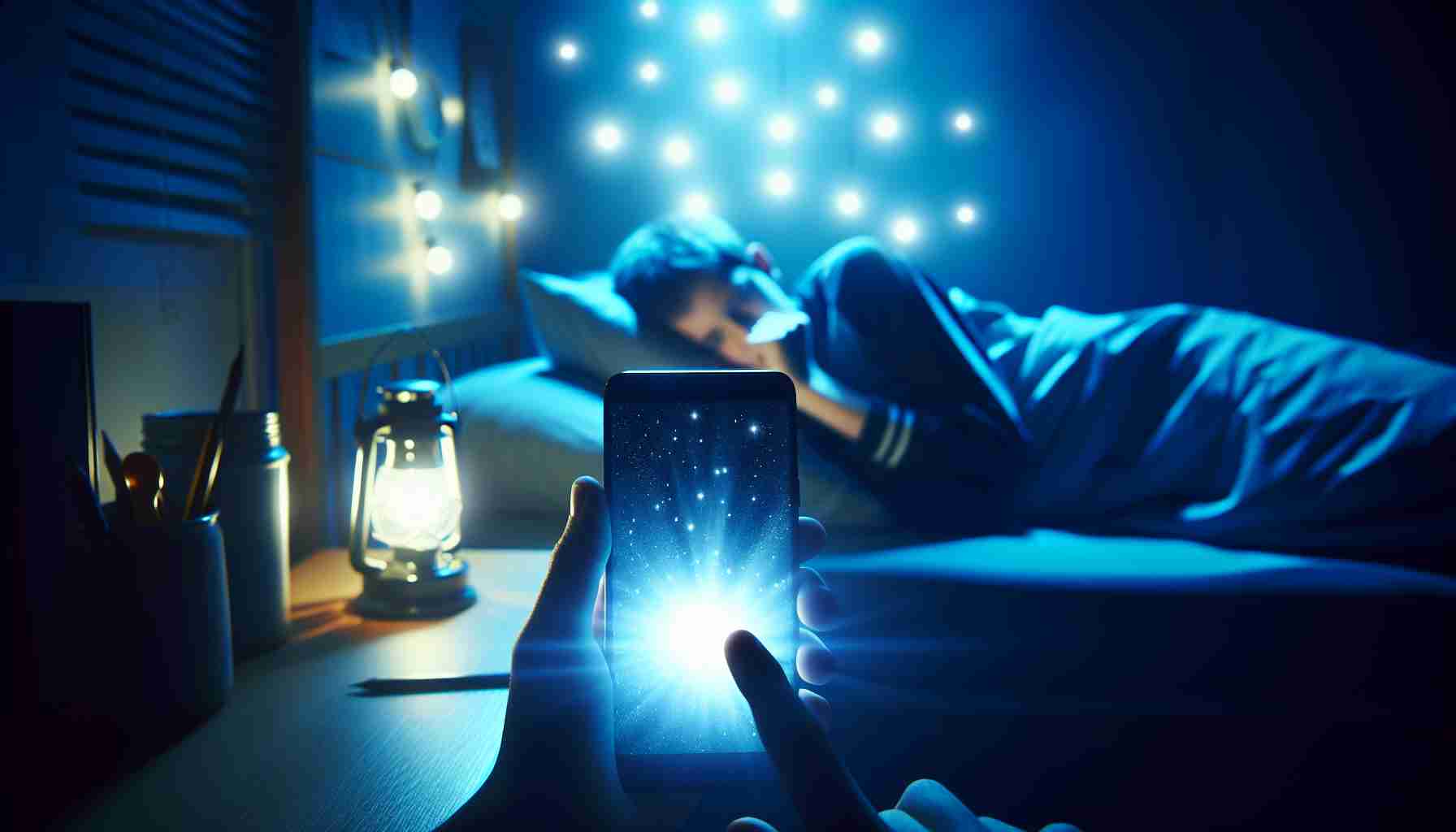
A recent study underscores a troubling link between smartphone usage and sleep quality among adolescents. Published in Jama Pediatrics, the research highlights concerns over the health of younger individuals amid increasing reliance on electronic devices. In Sweden, health authorities now advise against screen exposure for children under two years old, reflecting a growing movement among parents to limit such technology for their kids, reminiscent of the choices made by tech icons like Steve Jobs and Bill Gates.
Researchers from the University of Otago in New Zealand examined the habits of 79 adolescents aged 11 to 14. Their findings indicate that the most detrimental effects on sleep occur when teens use devices in bed, rather than during earlier hours. Interactive screen activities, such as gaming and multitasking, were found to disrupt slumber significantly, although even passive activities like watching movies were linked to shorter sleep durations.
In Italy, as students return to school, the Istituto Superiore di Sanità emphasizes the importance of preserving sleep for children. It warns that insufficient rest can lead to irritability and increased behavioral risks. Notably, a survey indicated that many preteens are already struggling with sleep, with about 50% of those at risk for social media addiction reporting less than six hours of sleep per night.
Internationally, movements against smartphone usage are gaining traction. Initiatives in the US, UK, and beyond reflect a broader recognition of the need to safeguard youth from the adverse effects of technology on their well-being and overall health.
The Impact of Smartphones on Youth Sleep Quality: A Growing Concern
As smartphones become increasingly ubiquitous in the lives of young people, the concern regarding their impact on sleep quality continues to grow. Recent studies have shed light on this issue, revealing alarming patterns that could have long-lasting effects on the health and well-being of today’s youth.
What specific effects do smartphones have on sleep?
Research indicates that smartphone usage, especially close to bedtime, can significantly interfere with the body’s natural circadian rhythms. The blue light emitted by screens can suppress melatonin production, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep. A survey conducted by the American Academy of Pediatrics found that nearly 75% of children have one or more electronic devices in their bedrooms, contributing to late-night usage and disrupted sleep patterns.
Why are young people particularly affected by smartphone usage?
Adolescents are in a critical developmental phase, both physically and psychologically, making them more susceptible to the negative effects of technology. The constant notifications and the fear of missing out (FOMO) can lead to anxiety and a compulsive need to check devices, even during the night. This behavior can contribute to a cycle of sleep deprivation, making it difficult for them to concentrate and perform academically.
What are the key challenges associated with smartphone usage and sleep?
One of the primary challenges is the difficulty in establishing boundaries between technology use and essential sleep. Additionally, social pressure and the desire for connectivity can drive adolescents to prioritize their devices over rest. Furthermore, parents may struggle to enforce healthy technology use patterns due to their own screen habits, creating an environment where poor sleep hygiene becomes the norm.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Smartphones for Youth
Advantages:
1. Access to Information: Smartphones provide instant access to educational resources, helping students with their studies.
2. Communication: They facilitate communication with peers and family, fostering connections that can enhance social support.
3. Entertainment: Mobile games and apps can offer fun and engaging recreational activities.
Disadvantages:
1. Sleep Disruption: As mentioned earlier, late-night usage can lead to insomnia and decreased sleep quality.
2. Mental Health Issues: Excessive smartphone use has been correlated with increased anxiety, depression, and social isolation among youth.
3. Decreased Physical Activity: Extended screen time can lead to a sedentary lifestyle, adversely affecting physical health.
Conclusion
As society grapples with the impact of smartphones on youth, it becomes essential to strike a balance between leveraging technology for educational and social benefits while also protecting the health and well-being of young individuals. Parents, educators, and policymakers must work collaboratively to promote healthy technology usage and ensure that sleep remains a priority for young people.
For more information on this pressing issue, please visit:
American Academy of Pediatrics
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Sleep Foundation