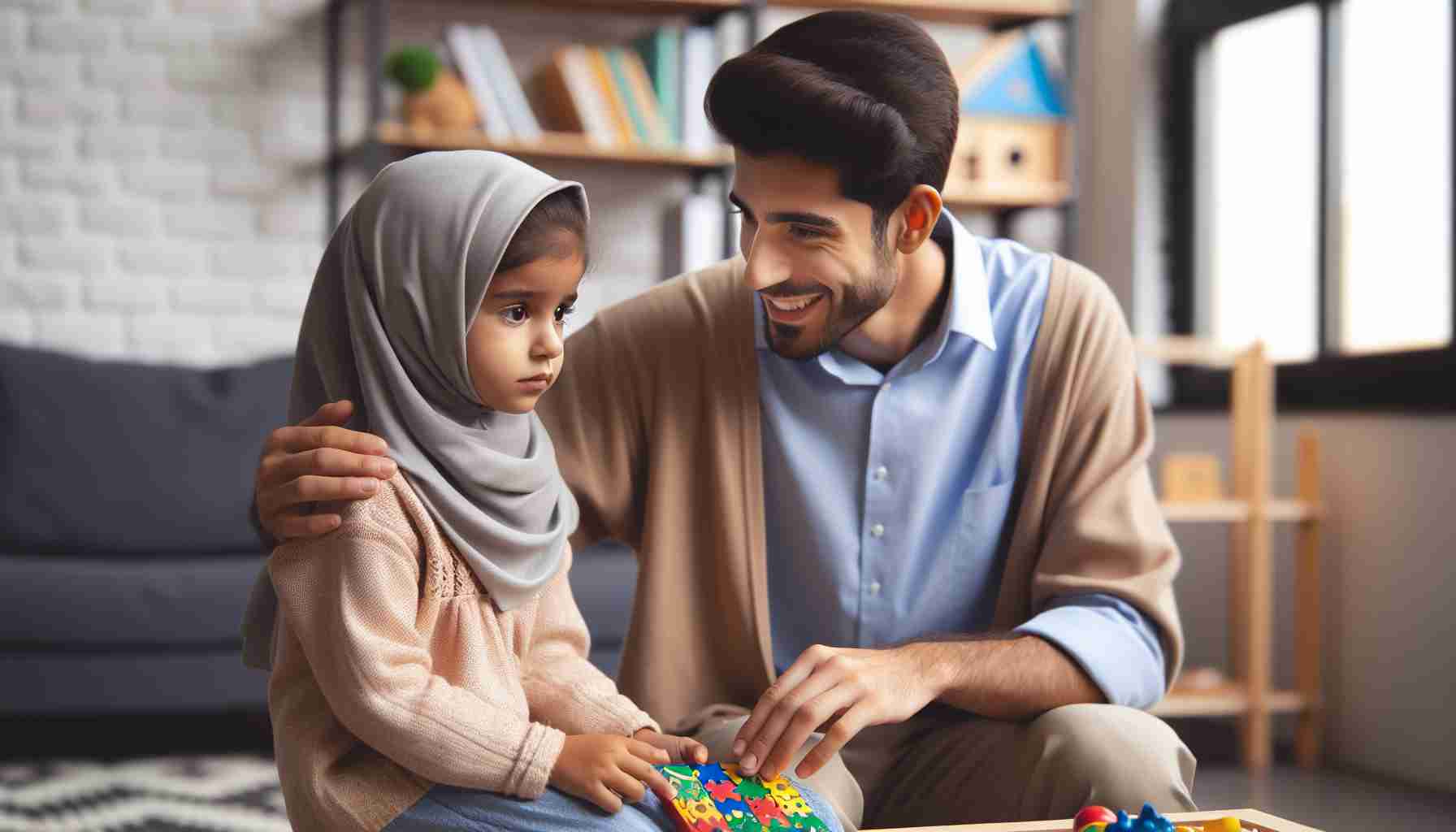
Childhood attention issues are a common concern for many parents and teachers worldwide. These challenges can stem from various factors. Instead of simply categorizing them as hyperactivity disorders, it’s essential to consider a holistic view of the child’s development and environment.
Research indicates that genetic, neurobiological, and social factors may contribute to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The development of the brain, particularly the frontal lobe, plays a critical role in attention regulation. Understanding these complexities can help tailor interventions to support children effectively.
Addressing attention difficulties in children requires a multi-faceted approach involving healthcare professionals, families, educators, and the individuals themselves. By creating nurturing environments at home and in school, promoting healthy habits, and personalized treatment plans, children with attention challenges can be supported in reaching their full potential.
Treatment strategies may vary based on age, with a focus on alleviating core symptoms and enhancing overall functioning. Behavioral therapy, medication, and psychological interventions can all play a role in managing ADHD. Early detection and intervention are key to providing children with the necessary tools to thrive academically and socially.
Exploring Comprehensive Approaches to Childhood Attention Difficulties
Childhood attention issues encompass a wide spectrum of challenges that can impact a child’s learning, behavior, and overall well-being. While the previous article touched on the genetic, neurobiological, and social factors contributing to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), there are additional dimensions to consider when understanding and addressing these difficulties in children.
What are the most important questions surrounding childhood attention difficulties?
One crucial question is the role of environmental factors in the development of attention issues. Research suggests that factors such as exposure to toxins, early childhood trauma, and parenting styles can influence a child’s attention and focus. Understanding how these external influences interact with genetic predispositions is essential in providing personalized interventions.
What are some key challenges or controversies associated with the topic?
One significant challenge in addressing childhood attention difficulties is the potential overdiagnosis and overmedication of children with ADHD. There is ongoing debate about the appropriate criteria for diagnosing ADHD and the risks and benefits of long-term medication use. Balancing the need for effective treatment with concerns about medication side effects and stigma is a crucial aspect of managing childhood attention issues.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of different treatment strategies for childhood attention difficulties?
Behavioral therapy offers advantages such as teaching children coping strategies and improving self-regulation skills. However, it can be time-intensive and may not always be accessible to all families. Medication, on the other hand, can provide rapid symptom relief but comes with the risk of side effects and the need for ongoing monitoring. Psychological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can address underlying emotional issues but may require long-term commitment.
In navigating the complexities of childhood attention difficulties, it is essential to consider a balanced approach that integrates various treatment modalities while prioritizing the child’s overall well-being and quality of life.
For more information on understanding and addressing childhood attention difficulties, visit Psychology Today for insights from experts in the field.