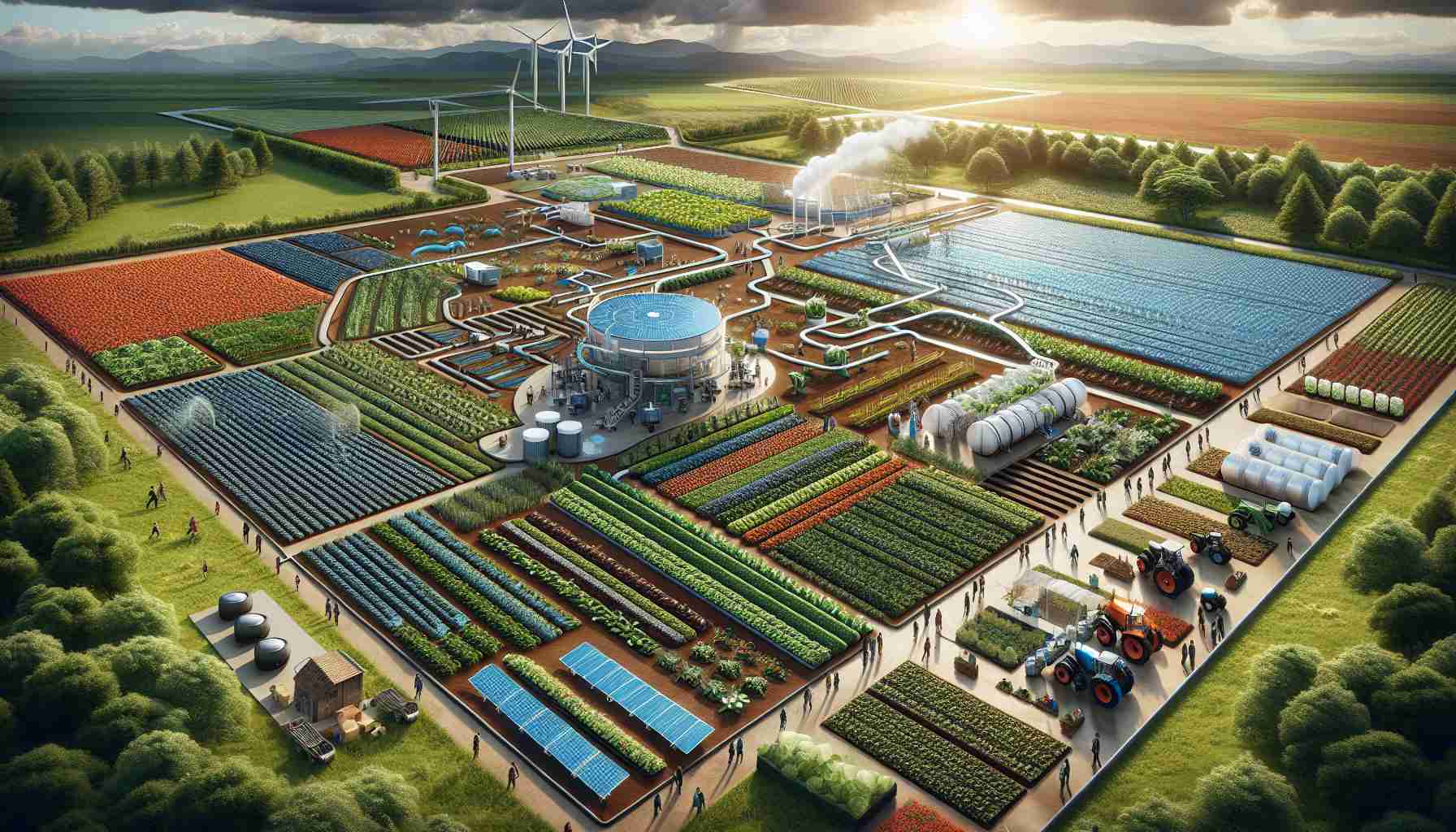
In recent years, the agricultural sector has witnessed a substantial shift towards environmentally friendly practices. Farmers and agricultural experts are increasingly adopting sustainable farming techniques to address climate change and preserve natural resources. This movement is gaining traction as more individuals recognize the importance of reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional farming methods.
One significant trend is the use of regenerative agriculture, which focuses on enhancing soil health through crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage. These practices not only improve soil fertility but also promote biodiversity and carbon sequestration, creating a healthier ecosystem.
In addition, vertical farming is emerging as a revolutionary solution, particularly in urban areas where space is limited. This innovative approach allows for the cultivation of crops in stacked layers, often using hydroponics or aeroponics, thereby minimizing water usage and maximizing output.
Moreover, agroforestry, the integration of trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, is gaining popularity for its dual benefits of crop production and forest conservation. This method provides shelter for crops, enhances soil quality, and supports wildlife habitats.
As the global population continues to grow, the importance of sustainable practices in agriculture cannot be underestimated. Collaborative efforts among farmers, scientists, and policy-makers are necessary to ensure that future generations can meet their food needs without compromising the health of the planet. Through innovation and commitment, the farming community is paving the way for a sustainable agricultural future.
Innovative Strategies for Sustainable Farming: New Horizons in Agriculture
As the demand for food continues to rise alongside a burgeoning global population, the agricultural sector is forced to innovate and adapt to meet these challenges sustainably. Various innovative strategies are emerging, beyond those previously noted, that are vital for fostering sustainable and resilient agricultural practices.
What are some innovative technologies transforming sustainable farming?
One major technological advancement revolutionizing sustainable farming is the implementation of precision agriculture. This technique uses data analytics, GPS, and IoT sensors to monitor and manage field variability in crops. By applying water, fertilizers, and pesticides only where necessary, farmers can significantly reduce waste, lower costs, and minimize environmental impact.
Another notable innovation is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in farming practices. AI systems can analyze weather patterns, soil health, and plant diseases, providing farmers with actionable insights to optimize their farming decisions. This ensures a more tailored approach to farming, enhancing productivity while reducing resource usage.
What are the key challenges associated with sustainable farming?
Despite its potential, several challenges complicate the widespread adoption of sustainable farming practices. Access to funding and technology is a significant barrier, particularly for smallholder farmers in developing regions. Many of these farmers lack the financial resources needed to invest in new technologies or methods.
Additionally, there is a lack of education and training regarding sustainable practices. Without proper knowledge, farmers may be hesitant to abandon traditional methods they are familiar with, even if those methods are less environmentally friendly.
Controversies also arise around organic farming practices, such as the debate over biotech crops. While proponents of organic farming argue that it is the best option for sustainability, critics highlight that genetically modified organisms (GMOs) can contribute to higher yields and greater resistance to pests and diseases, thus potentially reducing the need for chemical interventions.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of these sustainable strategies?
One of the most significant advantages of sustainable farming strategies is their capacity to enhance biodiversity and soil health. Techniques like agroecology, which emphasizes understanding complex ecosystems and utilizing natural processes, lead to resilient agricultural systems. These systems can better withstand environmental stresses such as droughts and floods.
However, the disadvantages can be pronounced, particularly concerning the initial transition costs. Farmers may face higher costs in the short term as they invest in new equipment, training, or organic inputs. Furthermore, the learning curve associated with implementing new methods can result in temporary lower yields.
Why is collaboration paramount in sustainable farming innovation?
Collaboration between various stakeholders—farmers, researchers, entrepreneurs, and policymakers—is crucial for the development and dissemination of sustainable farming practices. Through partnerships, knowledge sharing, and financial support, innovative ideas can be tested, refined, and scaled. For instance, governmental policies can offer incentives for farmers to adopt sustainable practices, while research institutions can provide the necessary scientific backing.
As communities engage in dialogue on sustainability, successful case studies can be spotlighted, demonstrating that sustainable farming is not only possible but profitable. The need for collective action becomes even more pressing as global challenges such as climate change and food insecurity loom on the horizon.
In conclusion, while the road to sustainable farming presents distinct challenges, the innovations emerging in this space hold considerable promise. By embracing technology, fostering education, and building collaborative networks, the agricultural sector can usher in a new era of sustainability that not only meets the demands of today but also secures a food-rich planet for future generations.
For more information on sustainable farming, visit FAO and discover various initiatives and resources dedicated to agricultural development and sustainability.